Nepal
Nepal is a founding member of the SASEC Program, joining with Bangladesh, Bhutan and India in 2001 to form this project-based partnership. Maldives and Sri Lanka became full members of SASEC in May 2014, following several years as active observers.
Nepal's new constitution, proclaimed in 2015, paves the way for rapid and inclusive economic growth. The Fifteenth Plan 2020/21–2024/25 aims to generate employment and achieve minimum average economic growth of 9.4% per annum. Nepal's vision for 2030 is helping the country work toward graduation from its least developed country status by 2022, achieving the Sustainable Development Goals, and becoming a middle-income country by 2030.
SASEC Projects in Nepal
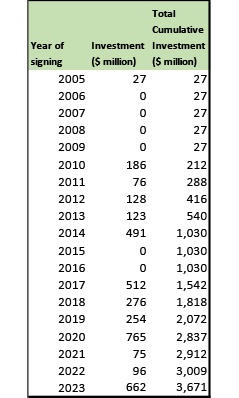
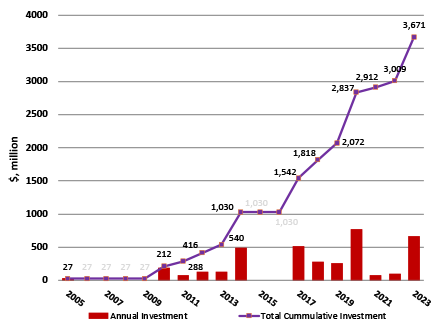
Since 2005, the Government of Nepal has signed 24 ADB-financed SASEC investment projects worth around $3.42 billion.
In addition to the projects, ADB-financed technical assistance has supported SASEC investment projects in Nepal, regional cooperation forums and knowledge-sharing initiatives, and pilot projects since 2001. A total of 26 national technical assistance projects (worth over $28.53 million) have assisted Nepal in project preparation, strategic planning, and capacity building.
Trade Snapshot
Direction of Intra-regional Trade
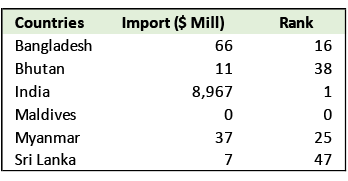
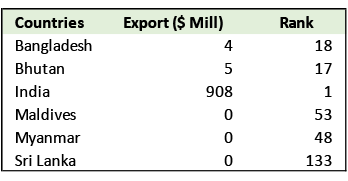
The value of Nepal's merchandise exports and imports trade with other SASEC countries, using International Monetary Fund data from 2023, is captured in the tables below.
Nepal's top import source worldwide is India, with imported goods valued at around $9 billion.
India is Nepal's largest export market worldwide, with exports valued at $908 million. Bhutan is its 17th top export market, with exports valued at $5 million. Bangladesh is its 18th top export market, with exports valued at $4 million.
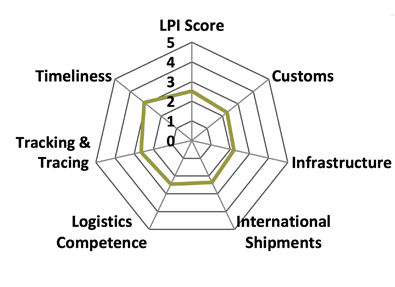
Logistics Performance Index (LPI)
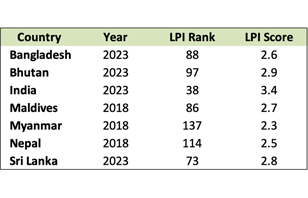
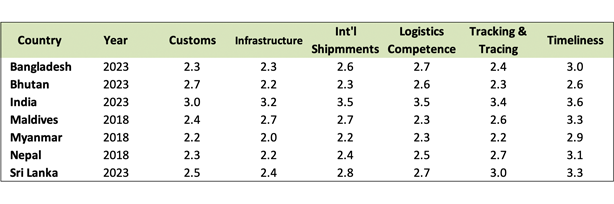
Nepal's overall LPI score for 2018 is 2.51, a significant improvement from its 2016 score of 2.38. The country climbed 10 spots to 114 out of 168 economies, from 124th place in 2016. Improvements in customs efficiency, customs clearance procedures, trade-related infrastructure, and ease of doing cross-border trade account for the improved 2018 score for Nepal.
Source: World Bank LPI (accessed May 2023)
Note: The LPI overall score reflects perceptions of a country's logistics based on six core dimensions: (i) efficiency of customs clearance process, (ii) quality of trade- and transport-related infrastructure, (iii) ease of arranging competitively priced shipments, (iv) quality of logistics services, (v) ability to track and trace consignments, and (vi) frequency with which shipments reach the consignee within the scheduled time. The scores for the six areas are averaged across all respondents and aggregated to a single score using principal components analysis. A higher score indicates better performance.

Economic Outlook

Gross domestic product (GDP) in Nepal is estimated to grow by 3.6% in fiscal year (FY) 2024 and 4.8% in FY2025, with the ramping up of hydroelectric production, the revival of domestic demand, and the recovery in tourism. Inflation in Nepal is projected at 6.5% in FY2024 and 6.0% in FY2025.
Source: Asian Development Outlook April 2024 (ADB)

Real GDP in Nepal is forecast to increase to 3.3% in FY2023-2024 with 2023’s lifting of trade and currency restrictions support economic recovery in the country. Growth will further increase to 4.6% in FY2024-2025, with a projected growth in hydropower exports as well as in the services sector. A predicted rise in tourist arrivals will benefit accommodations and services and the increase in electricity generation will support construction of new five-star hotels. The World Bank project’s Nepal’s consumer price inflation to remain high in FY2024.
Source: South Asia Development Update April 2024 (WB)